 A dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions can be recommended for several reasons. The main one is the presence of a caries which infect or destroy a major part of the structure of the tooth and do not restore it. It is the same for a tooth showing a deep crack. A gingiva disease can also make a mobile and painful tooth.
Finally, at some malposition of the teeth concerning the children, it may be necessary to conduct an extraction before orthodontic treatment.
The extraction of a tooth is always preceded by a questionnaire (research bleeding risk) and a radiograph.
This radiological examination will determine whether to proceed to a simple extraction or surgical extraction.
Impacted teeth, including wisdom teeth which often suffer from growth defects are extracted if their position causes problems.
In implantology it is sometimes necessary to extract the tooth in order to put an implant.
Finally, at some malposition of the teeth concerning the children, it may be necessary to conduct an extraction before orthodontic treatment.
The extraction of a tooth is always preceded by a questionnaire (research bleeding risk) and a radiograph.
This radiological examination will determine whether to proceed to a simple extraction or surgical extraction.
A dental extraction is the removal of a tooth from the mouth. Extractions can be recommended for several reasons. The main one is the presence of a caries which infect or destroy a major part of the structure of the tooth and do not restore it. It is the same for a tooth showing a deep crack. A gingiva disease can also make a mobile and painful tooth.
Finally, at some malposition of the teeth concerning the children, it may be necessary to conduct an extraction before orthodontic treatment.
The extraction of a tooth is always preceded by a questionnaire (research bleeding risk) and a radiograph.
This radiological examination will determine whether to proceed to a simple extraction or surgical extraction.
Impacted teeth, including wisdom teeth which often suffer from growth defects are extracted if their position causes problems.
In implantology it is sometimes necessary to extract the tooth in order to put an implant.
Finally, at some malposition of the teeth concerning the children, it may be necessary to conduct an extraction before orthodontic treatment.
The extraction of a tooth is always preceded by a questionnaire (research bleeding risk) and a radiograph.
This radiological examination will determine whether to proceed to a simple extraction or surgical extraction.
Simple extractions
 Simple extractions are performed on teeth that are visible in the mouth, which are not excessively damaged by caries and can be extracted without complication.
The operation is painless, it's performed under local anesthesia. After ensuring the insensitivity of the gingiva, the dentist can extract the tooth.
Simple extractions are performed on teeth that are visible in the mouth, which are not excessively damaged by caries and can be extracted without complication.
The operation is painless, it's performed under local anesthesia. After ensuring the insensitivity of the gingiva, the dentist can extract the tooth.
Surgical extractions
 If the tooth can not be removed in the traditional way, it is necessary to perform surgical removal.
Surgical extractions involve the teeth with difficult access, which have very divergent or curved roots of teeth that are significantly damaged (severe decay for example).
The operation starts again by a local anesthetia then the dentist makes an incision in the gums and the bone tissue around the tooth.
Once the tooth is removed, the cavity is cleaned. If a tooth suffering from inflammation, the damaged tissue will also be removed.
Closing the cavity is effected using sutures for joining the edges of the gums.
If the tooth can not be removed in the traditional way, it is necessary to perform surgical removal.
Surgical extractions involve the teeth with difficult access, which have very divergent or curved roots of teeth that are significantly damaged (severe decay for example).
The operation starts again by a local anesthetia then the dentist makes an incision in the gums and the bone tissue around the tooth.
Once the tooth is removed, the cavity is cleaned. If a tooth suffering from inflammation, the damaged tissue will also be removed.
Closing the cavity is effected using sutures for joining the edges of the gums.
Treatment after extraction
Bleeding In healthy subjects the bleeding stops 3-4 minutes after extraction, but dripping or oozing blood may continue for 48 hours. Bleeding will be controlled by putting gauze on the site of the extraction and closing the mouth to create pressure. Swelling A temporary minor swelling may occur and will be limited by the application of ice (wrapped in a cloth). Pain Take the prescribed analgesics without waiting the possible appearance of pain. Risk of infectionAn antibiotic will be given if necessary.
In some situations, it is essential that a tooth is extracted. If today extraction is a common and painless operation, everyone wants to avoid is noticed this missing tooth in his smile.
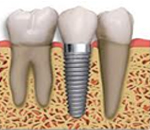
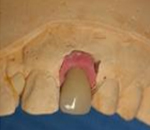 Especially if the extracted tooth is in the smile zone, solutions will be proposed to avoid this is noticed missing tooth.
It is important to consider before the extraction the need to remplace the extracted tooth by a temporary tooth or transitional prostheses if several teeth.
These prostheses may be attached to adjacent teeth, or on removable plates on implants in some situations.
If it's about many teeth, then a number of solutions are distinguished.
Fixed prostheses
Especially if the extracted tooth is in the smile zone, solutions will be proposed to avoid this is noticed missing tooth.
It is important to consider before the extraction the need to remplace the extracted tooth by a temporary tooth or transitional prostheses if several teeth.
These prostheses may be attached to adjacent teeth, or on removable plates on implants in some situations.
If it's about many teeth, then a number of solutions are distinguished.
Fixed prostheses 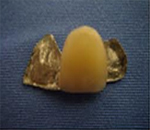 It is placed as a temporary bridge on the adjacent teeth tooth extracted. This temporary bridge can be prepared in the dental laboratory or directly in the mouth at the time of the intervention.
It is made of resin, a color similar to that of adjacent teeth. The bridge remains in place for the duration of the healing of the extracted tooth.
The removable prostheses
It is placed as a temporary bridge on the adjacent teeth tooth extracted. This temporary bridge can be prepared in the dental laboratory or directly in the mouth at the time of the intervention.
It is made of resin, a color similar to that of adjacent teeth. The bridge remains in place for the duration of the healing of the extracted tooth.
The removable prostheses It is most often used when several teeth are to be extracted. The prosthesis must be planned in advance and conducted in the laboratory. We adapt, immediately after the extraction, on the gums which healing is facilitated by the use of a soft resin.
These transitional prosthesis placed during healing, will be replaced after a few months (2-6 months) by definitive prostheses.
It is most often used when several teeth are to be extracted. The prosthesis must be planned in advance and conducted in the laboratory. We adapt, immediately after the extraction, on the gums which healing is facilitated by the use of a soft resin.
These transitional prosthesis placed during healing, will be replaced after a few months (2-6 months) by definitive prostheses.








