 Any dental trauma in children as in adults, requires the advice of a dentist, with a radiological examination and monitoring over time
The front teeth (incisors and canines) are the most exposed. From the falls in the playground to the bicycle accidents, skiing, skating ... young children and adolescents are the most exposed for risk of injury.
Domaged tooth is threatened to lose it's vitality. This domage of the dental pulp can cause abscess formation and, ultimately, destruction of the root and tooth lost.
The main problem is the permanent teeth but be aware that achieving a baby tooth can effect on the successor tooth.
Previous permanent teeth appear between 4 and 6 years. If we have doubt we must consider that the traumatized tooth is a permanent tooth.
Any dental trauma in children as in adults, requires the advice of a dentist, with a radiological examination and monitoring over time
The front teeth (incisors and canines) are the most exposed. From the falls in the playground to the bicycle accidents, skiing, skating ... young children and adolescents are the most exposed for risk of injury.
Domaged tooth is threatened to lose it's vitality. This domage of the dental pulp can cause abscess formation and, ultimately, destruction of the root and tooth lost.
The main problem is the permanent teeth but be aware that achieving a baby tooth can effect on the successor tooth.
Previous permanent teeth appear between 4 and 6 years. If we have doubt we must consider that the traumatized tooth is a permanent tooth.
Expulsion of a tooth
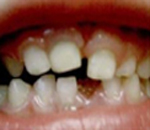 1) Retrieve the tooth, caching it from the end
2) Do not clean or scratch the root
3) If possible replace the tooth in its bony socket
If this is not possible, therefore, put the tooth directly into the patient's mouth (under the tongue) ensuring that it will not swallow it, and this of course if he is not unconscious
If not it must be placed in a saline solution or milk, or put the tooth in cling film and mastering the bleeding with gauze or a clean handkerchief
In both cases, relocation, if possible, should be done very quickly and within a period of 1 hour.
If we are not avalibal, you need to contact immediately a dentistry service, stomatology or ENT to the nearest hospital.
1) Retrieve the tooth, caching it from the end
2) Do not clean or scratch the root
3) If possible replace the tooth in its bony socket
If this is not possible, therefore, put the tooth directly into the patient's mouth (under the tongue) ensuring that it will not swallow it, and this of course if he is not unconscious
If not it must be placed in a saline solution or milk, or put the tooth in cling film and mastering the bleeding with gauze or a clean handkerchief
In both cases, relocation, if possible, should be done very quickly and within a period of 1 hour.
If we are not avalibal, you need to contact immediately a dentistry service, stomatology or ENT to the nearest hospital.
Fracture a piece of tooth enamel
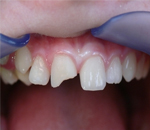 Suivre le même processus qu’avec une dent expulsée : récupérer le morceau fracturé qui pourra éventuellement être recollé et le conserver dans la bouche ou dans du lait.
Consulter rapidement.
La dent est alors reconstituée avec un matériau composite de la même couleur que l’émail.
Suivre le même processus qu’avec une dent expulsée : récupérer le morceau fracturé qui pourra éventuellement être recollé et le conserver dans la bouche ou dans du lait.
Consulter rapidement.
La dent est alors reconstituée avec un matériau composite de la même couleur que l’émail.
tooth in movement
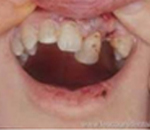 The displaced tooth is mobile: the emergency action is, to put it in the right place with finger pressure, taking care not to aggravate the injury.
The displaced tooth is stable: it is better not to touch it and to consult a dentist very quickly.
The displaced tooth is mobile: the emergency action is, to put it in the right place with finger pressure, taking care not to aggravate the injury.
The displaced tooth is stable: it is better not to touch it and to consult a dentist very quickly.
Choc without immediate visible effect
 The patient must still to check with a dentist and, if necessary, be followed for a period of 1 year. A shock can have hidden consequences, such as a small crack, lesions at the root of the tooth pulp (nerve and vessels that supply the tooth). During this period, special attention will be paid to the teeth: pain or discoloration of the tooth will be the alert signals.
The patient must still to check with a dentist and, if necessary, be followed for a period of 1 year. A shock can have hidden consequences, such as a small crack, lesions at the root of the tooth pulp (nerve and vessels that supply the tooth). During this period, special attention will be paid to the teeth: pain or discoloration of the tooth will be the alert signals.








