The gums are a pink mucosal tissue surrounding the teeth. When undergoing an attack (infection, presence of calculus, ...) gingivitis develops.
What is gingivitis?
It is an inflammation of the gums, which swells, becomes dark red and bleeds at the slightest touch: brushing teeth, biting into an apple. Gingivitis is often located between two teeth. It can extend and even become widespread. Without treatment it favors loosening and can also accelerate the lost of teeth.
What is its origin?
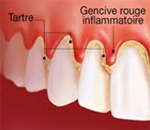
Usually gingivitis is caused by the presence of an excess of tartar, it self produced by the plaque. Plaque and tartar are supportive environments for the proliferation of bacteria, and therefore localized infection of the gums. Often linked to poor oral hygiene, gingivitis is however encouraged by some situations: pregnancy, smoking, diabetes, by incorrectly positioned teeth or bad decay treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of gingivitis is based on:
- Improved hygiene of the patient
- Careful scaling realized in the dental clinic
- Using mouth washer liquide
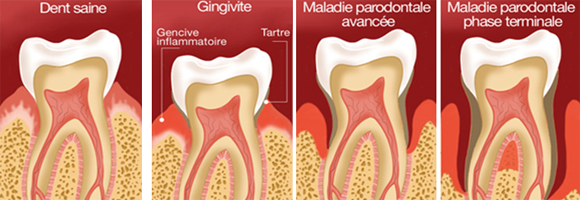
Originally, periodontitis is characterized by infection of the gums and the bone that surrounds the tooth. Infection leads to destruction of periodontal tissues that support the teeth (gums, cementum and jaw bone). As the disease progresses, a periodontal pocket forms between the gum and the tooth. She quickly became
What are the symptoms?
Large amount of bacteria and tartar which aggravates the irritation of the gums and prevents healing. At its most advanced stage, periodontitis causes tooth lost.
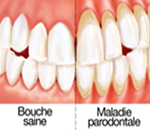 Among the telltale signs of a possible periodontitis:
red and swollen gums that bleed easily when brushing, tooth mobility, bad breath, gum abscess, gingival recession ... Aesthetically, the destruction of periodontal tissues can cause strong discomfort such as shrinkage of the gums.
Among the telltale signs of a possible periodontitis:
red and swollen gums that bleed easily when brushing, tooth mobility, bad breath, gum abscess, gingival recession ... Aesthetically, the destruction of periodontal tissues can cause strong discomfort such as shrinkage of the gums.
- Bad breath can be caused by gingivitis, periodontitis, dry mouth, tooth infection or by a stomach illness that causes regurgitation
- Review your dentist to diagnose the cause of bad breath
Aggravating factors of Gingivitis and periodontitis
- orthodontic treatment
- tobacco
- Dimensions and dental overlapping
- Removable Prosthodontics
- Unsuitable Dental Crowns
- Bruxism or teeth grinding
- Extrusion and Version teeth
- alcohol
- stress
- Pregnant Woman
- Pregnancy Gingivitis increases 7 times the risk of preterm delivery
- puberty
- menopause
- Menstruation
- Certain medications: oral contraceptives, antidepressants, antiepileptics ....
- Dietary imbalance favors or worsens periodontal disease
- Some general diseases increase the susceptibility of periodontal disease by altering the immune system
- Dysfunction of the thyroid and parathyroid
- Diabetes: Diabetic is a risk 3 times more important to develop periodontitis.
- leukemia
- Blown AIDS is associated with periodontal manifestations.
Periodontitis is an infection of periodontal tissues (gums and underlying bone) that support the teeth. Treatment is based on cleaning and disinfection.
Initial treatment of periodontitis
Disinfection of periodontal tissues together based on:
- The specific hardware home use to effectively clean teeth even in the most difficult areas
- An anti-infective therapy prescription of the practitioner. In some cases, the use of antibiotics may be considered
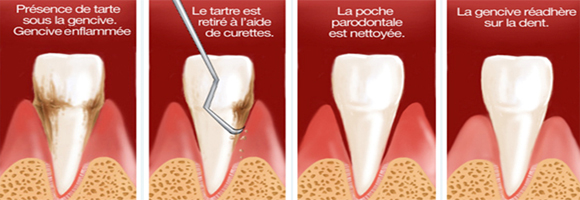
- Surfacing (or curettage) made in the dental clinic to disinfect and clean the areas under your gums.
Surfacing is complementary scaling. Non-surgical procedure, it helps to clean the surface of the tooth roots and gums thoroughly. The purpose is to disinfect the tissue and allow the closure of periodontal pockets, by a re-adhesion of the gingiva to the tooth surface. However, when the surfacing of all teeth is not sufficient to stabilize periodontitis, other therapies, including surgical (shreds sanitation), can then be considered.
How do we realize surfacing?
Large amounts of bacteria and tartar that have accumulated under the gums are removed after anesthesia. The proposed number of sessions can vary depending on the severity of periodontitis and the number of affected teeth. To complete subgingival disinfection, surfacing may be followed by irrigation of periodontal pockets with antiseptic.
 The effectiveness of this initial treatment is evaluated within a few weeks. If the infection persists in some areas, a second treatment, often surgery, could be proposed.
The effectiveness of this initial treatment is evaluated within a few weeks. If the infection persists in some areas, a second treatment, often surgery, could be proposed.
Surgical treatment of periodontitis
It allows, by lifting a gum, treat periodontitis more efficiently. In some cases, the lesions can be repaired with bone grafts or gums. Surgical treatment consists of making shreds sanitation The flaps are clean surgery to treat periodontitis (loosening of teeth). Directions The flaps sanitation are generally available in second-line treatment for periodontitis. They complete non-surgical treatment (planing) where the results obtained with it are not sufficient. Objectives The goal of this treatment is widely accessing tooth roots and bone that surrounds to clean effectively. During a sanitation flap, we have a direct view of the areas that we are cleaning, unlike root planing in which the cleaning is done only through the sense of touch. practice The procedure is done under local anesthesia. The gum is raised to put the root and the bone exposed, which allows a complete cleaning of the tooth surfaces. The shape of the bone surrounding the teeth may eventually be changed to improve treatment outcomes and facilitate oral hygiene.
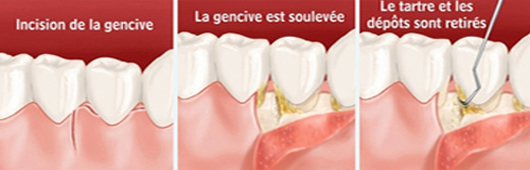
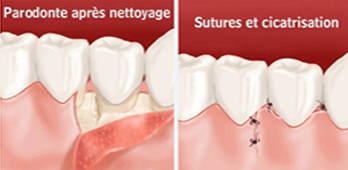
Maintaining results
To retain the benefit of treatment, periodontal maintenance therapy consists of cleaning and very regular dental cleanings should be set up with your dentist. The interview lasts a lifetime and must be followed with great care. This is probably the most important phase of treatment.








