Prosthetic crowns can reconstruct very dilapidated teeth, whether or not devitalized.
- The tooth is prepared and a temporary dental crown resin is introduced.
- If the tooth is devitalized, a pin is placed in the tooth, either directly or through a footprint of the inside of the root.
- A dental impression is taken and sent to the technician that he realizes the dental crown.
- The dental crown is placed after fitting.
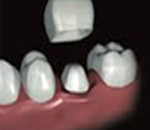
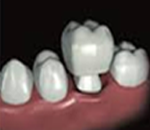
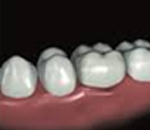
Dental resin crown or temporary dental crown
It protects the tooth during the design stages of the final dental crown. But with time, the resin becomes porous and microbes pass through so avoid to keep it long time.
The metallic dental crown

This is the least expensive of prosthetic dental crowns but less aesthetic. It nevertheless remains an excellent dental prosthesis. The metal used must be chosen wisely. Indeed, the presence in the mouth of many metals of different kinds can cause the appearance of a metallic taste or a slight tingling sensation. Its price and its color varies depending on the metal used (gold base alloy or not).
The metal-ceramic dental crown

It consists of a metal shell covered with a ceramic that has the same color as the tooth. The presence of metal in the ceramic does not provide the same degree of translucency as natural teeth which can give an opaque appearance to the crown. The metal substructure may be reflected over time due to the retraction of the gums.
The all-ceramic dental crown
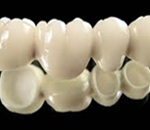
With a core based on alumina or zirconia *, it is covered with a veneering ceramic of the same color as that of the thus dent.C'est a dental crown without metal. Its composition, which does not absorb light, retrieves the translucency of a natural tooth. Specificity
- High biocompatibility: no metal-related allergy, no interaction with other restorative materials
- Resistance and stability in the long term
- Important mechanical properties which allows the realization of single crowns but also for small bridges extended
- No visible transition at the gum edge (no gray piping appearing at its base)
A bridge is a fixed prosthesis to replace one or more missing teeth by building on the adjacent teeth.
Adhesive bridges
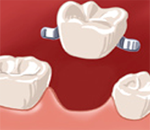
Adhesive bridges allow the replacement of a single tooth (or two in some cases) based on the adjacent teeth with metal fins glued. When laying a bridge is possible, it is a very aesthetic and little decaying solution for adjacent teeth on which is anchored. The prosthetic tooth may be of metal or ceramic lined. However, the fins can not be covered with ceramic tiles. They are therefore metallic color but are usually not visible or very discreet.
Conventional bridges
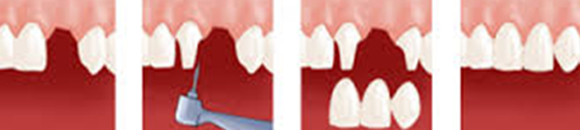
For this type of bridge, anchoring on the teeth along the tooth gap is most often through dental crowns and sometimes with inlays or onlays. In the same way that dental crowns, bridge elements can be metal, metal-ceramic or all-ceramic (in some cases only). The steps of forming bridges are the same as those of the anchor means available: dental crowns, inlays or onlays. The teeth that line the missing tooth is prepared to receive the bridge.
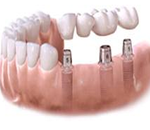
With the advent of dentures on implants, the number of bridges made tends to decrease. Indeed, when a bridge is made, the teeth that support must be prepared and then have to bear the burden of the replaced teeth. With implants, you do not touch the neighboring teeth and chewing forces are supported by implants. They thus preserve the future of the neighboring teeth and the alveolar bone that supports them.
Inlays and onlays are alternatives to fillings or large volume of resins, and sometimes help prevent a prosthesis require extensive tooth preparation.
Why inlay / onlay rather than simply filling or dental resin?
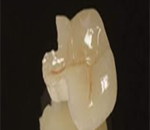
The mechanical strength of inlays and onlays is much better than dental fillings and resins made directly to the firm by conventional techniques. Furthermore, inlays and onlays possible to obtain a better seal with a conventional sealing. contact point of reliability is thus increased with the adjacent teeth, which reduces the risk of caries and gingival inflammation recovery problems. In the case of large volume of caries, achieving an inlay or onlay can often avoid to make a dental crown that would result in a greater decay of your tooth.
Inlays, onlays and aesthetics
For strength issues, inlays and onlays are made systematically metal. One can now fabricate highly aesthetic inlays and onlays, composite resin or ceramic, which exactly replicate the color and shape of your teeth.
Technical realization:
First session: the tooth is prepared
By cleaning decay and by carving a cavity that host:
- The inlay when the cavity is located within the walls of the tooth
- The onlay when the cavity includes one or more walls.
Second session: the inlay is placed and glued in the cavity of the tooth. Unlike traditional fillings, inlays / onlays do not exert pressure on the remaining dental walls (risk of fracture). The chemical adhesion to dental consolidates all sides and provides a better seal that blocks bacterial infiltration.








